History:
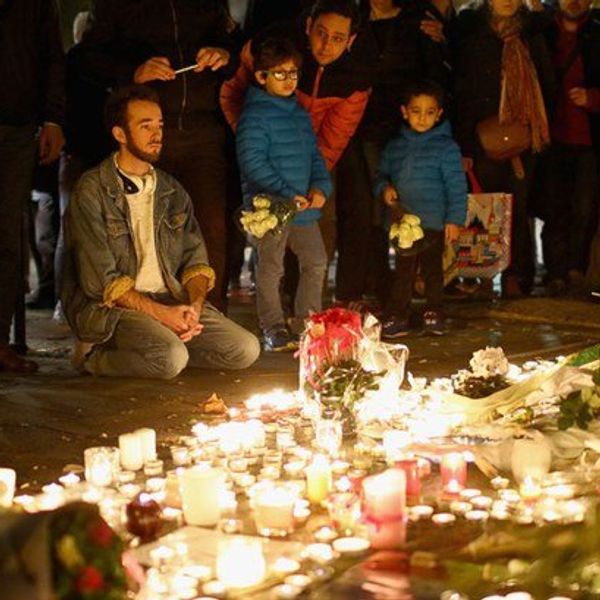
Due to the religious divide between the Sunni Muslims in the South and the Shia Muslims in the North, much tension has existed in Yemen since the 1900s. The disunity throughout the country relating to tribalism, poverty, and an unstable government has made civil war inevitable.
After President Saleh resigned from his position due to the proliferating violence and disagreements in Yemen, he has sided with Houthis, a Shia group, hoping to regain his power. In the South, the Sunni Muslims have been supported by the newly chosen president, Hadi, and the Yemeni government. A Saudi-led coalition aided by many other Middle Eastern countries and the United States has helped the new Yemeni government. Beyond the Middle East, Great Britain and France have sent intellectual aid to the Sunni while China helps support the infrastructure of Yemen. As more parties become involved, Yemen has shifted from civil war to a major front on the War on Global Terror.
What the UN has done:
The crisis in Yemen involves such a vast number of countries because it affects every region in different ways. For example, western countries fear the threat of attacks arising from certain terrorist groups as the country becomes more unstable. Overall, the United Nation has taken little action on this urgent issue. Although it is concerned with addressing humanitarian issues and offering peaceful negotiations, it refuses to send an international peace-keeping military. The largest action it has taken is when the United Nations Security Council issued a statement urging an end to all violence. However, the written statement had little effect on the crises throughout the country. The brutality remains as strong as ever.
Certain branches of the UN have been involved, however. The UN Human Civil Rights Office is monitoring the war to ensure there are no harsh war crimes committed by any party while the UN High Commissioner for Refugees is trying to find a solution for the increasing number of Syrian, Somali, Yemeni, and Ethiopian refugees moving into Europe.
United States’ Views and Actions
Since the emergence of the conflict, the United States has expressed deep concern for the high level of violence in the area. Once on good terms with President Saleh, the United States pushed for him to sign the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), an alliance amongst some of the Middle Eastern countries. However, after Saleh refused the proposal, United States took this as a denial to help maintain peace in the area. As Saleh rejected the alliance three times and did little to lessen the evident violence in the region, the United States has shifted its support to Hadi and the Sunni Muslims in hopes that they would help fulfill the peace of Yemen. Also, the support of the South by the United States is, in part, due to the Sunni’s more Western-influenced ideals after the British impact over Yemen in the early 1900s.
Currently, the United States has joined the Saudi-led coalition. The main interest of the United States is to restore peace and stability in the Middle East. That way the United States can ensure the peace of the future of its citizens.. With its vast troops, resources, political strength, and intellectual capabilities, the United States hopes to greatly aid Yemen in achieving peace. The United States sincerely hopes other countries will consider aiding the Sunni Muslims and the Yemeni government in restoring stability in the Middle East. It especially calls upon the United Nations to send military aid to their forces in Yemen.
In regards to the citizens in the region of battle, the United States believes there should be more protection for these innocent individuals suffering from warfare. Many endure casualties due to war-inspired violence. Others starve from a lack of resources and a failing economy. There are some cities or villages trapped in the middle of severe battle zones. The United States pushes for more reinforcements for these suffering people in Yemen.