Space. It's so beautiful yet filled with mystery and discoveries yet to be made. What is interesting though, over the past hundreds of years of research from great minds like Galileo, Issac Newton, Hipparchus, and even Albert Einstein, astronomers still haven't fully answered one of the most basic questions, "What is our universe?" Even though astronomers don't completely know the answer, they have a pretty good idea. I'm gonna go over briefly the main principles of cosmology then focus one two of the most mysterious objects in the universe, dark matter and dark energy.
Cosmology
Because astronomers wanted to explore the question of "What is our universe?" and "How/When did it form?' they created a specific sub-field of study called Cosmology. It's mostly based on astronomical observations with explanations based on accepted and tested laws of physics.
Their core principle is that the laws of physics are universal, therefore, astronomers can determine how an object (a meteor, planet, star, galaxy, etc.) moves in the universe.
Galaxies far far away...
In 1920, there was a debate between two astronomers on the possibility of other galaxies beyond our own Milky Way Galaxy. It wasn't until famous astronomer, Edwin Hubble (you might have heard of the Hubble Space Telescope...) to prove there are other galaxies outside our own.
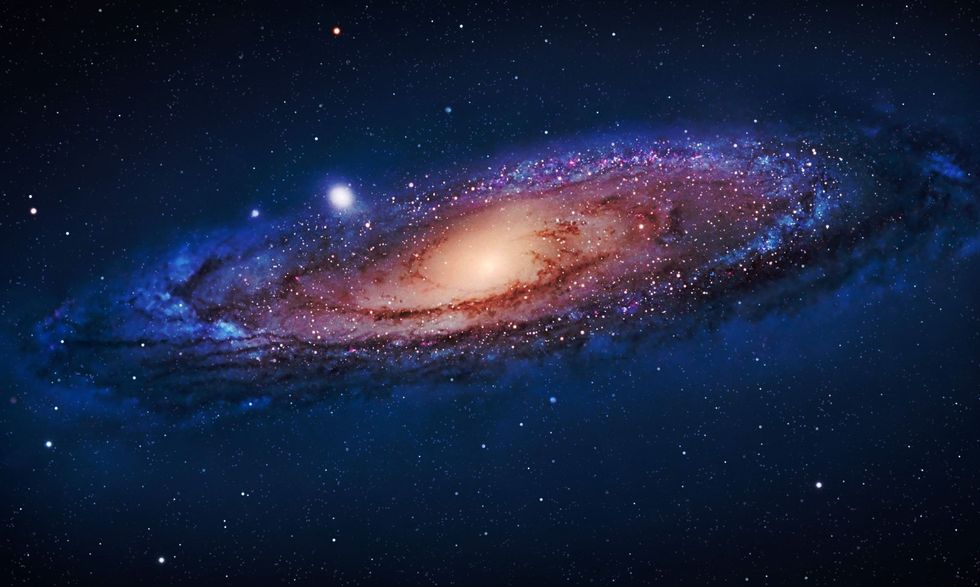
He found the Andromeda Galaxy, which is the closest galaxy, approximately 2.3 million light years away. That means it took 2.3 million years for the light from the galaxy to reach Earth. Therefore, we're looking back in time 2.3 million years ago! It is also said that in the future, the Andromeda galaxy will merge with our own Milky Way galaxy to create an even bigger galaxy!
After his discovery of the Andromeda galaxy, astronomers found a whole lot more galaxies since then. More like a 100 billion more. Some merging together, due to the force of gravity, to create larger galaxies. But, again, how did this happen?
The birth of the universe
A very, very long time ago, the universe was all close together so tightly and it was extremely hot. Many people think that there was already space outside of this heaping pile of gas but that's not the case. The universe itself was the heaping pile of gas. Astronomers called this point "the singularity". Then, with the formation of gravity, pressure built up inside and then exploded in an explosion some may call "The Big Bang".
That's when galaxies were formed and everything within them. It was mistakingly believed that the galaxies were moving apart and away from each other on their own. It's actually the universe itself moving and it keeps expanding, making galaxies further and further apart.
It is said that in the future, we won't be able to see other galaxies anymore because the universe will continue to expand forever.
Dark Matter
You may have heard of this before but what exactly is dark matter? Well, that's still being discovered to this day. No one really knows for sure right now. But if no one really knows for sure then how do we know it exists? You know that phrase, "Just because you can't see it, it doesn't mean it doesn't exist"? That's exactly how astronomers know it exists.
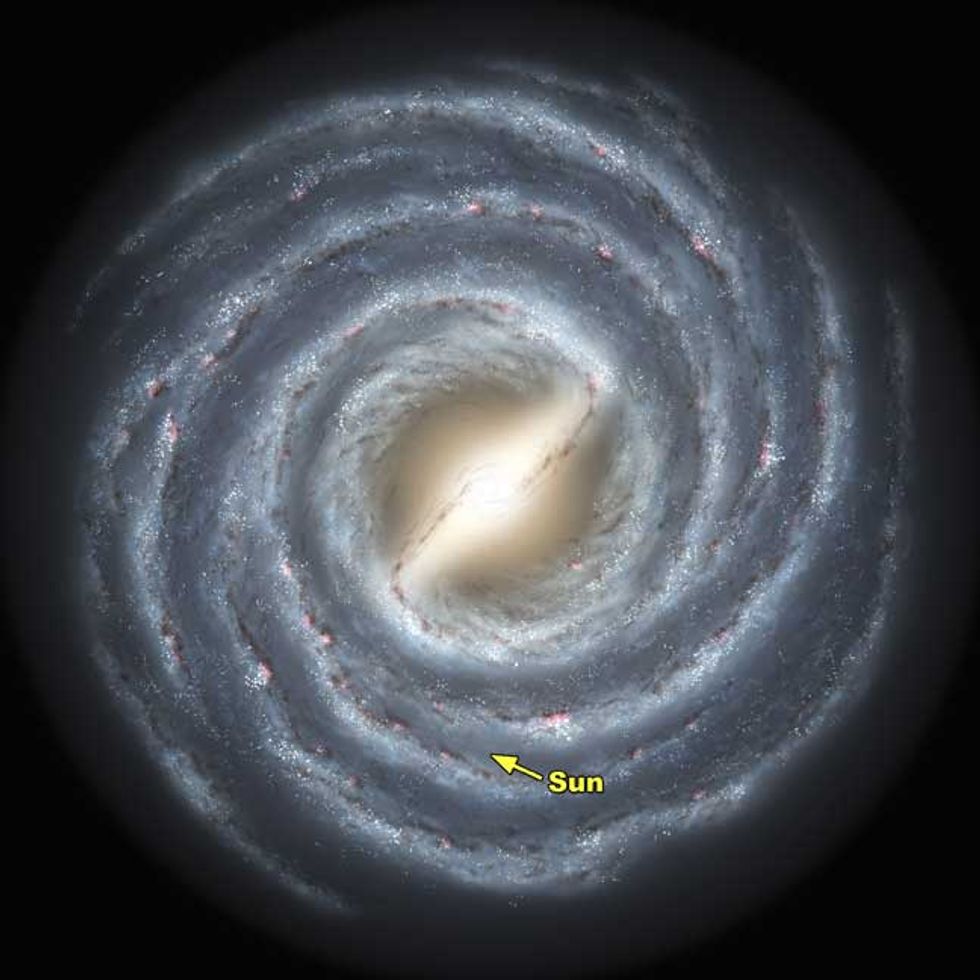
There's a weird thing our Milky Way galaxy does.
Instead of gravity moving the spiral arms on the outer rims of the galaxy slower than the center, the speed of the spiral arms remain consistent or even a little bit faster near the outer edge.
Astronomers were confused because there was already a law set in place that contradicts these actions. It's the law that our solar system follows. The farther away a planet is from the Sun, the slower it evolves around it. They thought the same law applies to our galaxy and it should! But our galaxy isn't following the law...so how...?
The only explanation is that there has to be a force of matter that is making the arms go at the same speed. This matter has no visible light or light radiation emitting from it.
That, my friends, is dark matter. It's actually said that there's more dark matter (four to every one star) than there is luminous matter (matter that we can see with light/radiation).
Astronomers are trying really hard to find stronger evidence to further prove its existence but it will take more advanced technology and methods. For now, it's just a theory but we're getting closer each day!
Dark energy
No, I'm not talking about evil ghosts. I'm talking about the fact the universe continues to expand at an accelerating rate. Astronomers thought that over time, after the big bang, the expansion will slow down. So what is causing this acceleration?
Dark energy. An "antigravity" force that emits no visible light or radiation. Same as dark matter, there's still no answer for dark energy to this day.