play a crucial role in assessing the financial health of a company.
Business liquidity is essential for the survival and success of any organization. Liquidity ratios play a crucial role in assessing the financial health of a company. They provide insight into a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations and manage its cash flow effectively. In this blog post, we will discuss what liquidity ratios are, why they are important, what they are used for, and how to assess a company's liquidity.
What are Liquidity Ratios?
Liquidity ratios are financial ratios that measure a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations. These ratios indicate whether a company has enough current assets to pay off its current liabilities.
Current assets are assets that can be converted into cash within one year, while current liabilities are
liabilities that are due within one year. Liquidity ratios can be divided into two categories: current liquidity ratios and acid-test or quick ratios.
Current Liquidity Ratios
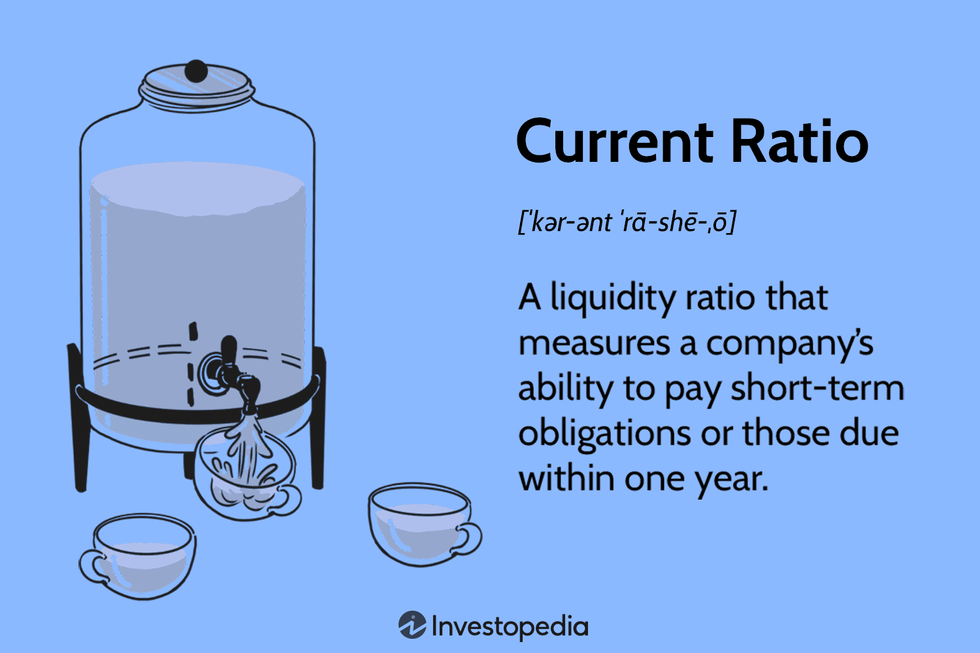
Current liquidity ratios compare a company's current assets to its current liabilities. They provide an overview of a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations. The most commonly used current liquidity ratios are the current ratio and the quick ratio.
The current ratio is calculated by dividing a company's current assets by its current liabilities. It indicates whether a company has enough current assets to cover its current liabilities. A current ratio of 2:1 or higher is considered healthy, while a current ratio of less than 1:1 is considered risky.
Quick Ratio
The quick ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio, is a more conservative measure of a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations. It is calculated by subtracting inventory from current assets and then dividing the result by current liabilities. Inventory is excluded from the calculation because it is not easily converted into cash. A quick ratio of 1:1 or higher is considered healthy, while a quick ratio of less than 1:1 is considered risky.
Acid-test or Quick Ratios are similar to current liquidity ratios, but they exclude inventory from current assets. This ratio is an indicator of a company's ability to pay off its current liabilities with its most liquid assets.
Why are Liquidity Ratios Important?
Liquidity ratios are important for several reasons. Firstly, they provide insight into a company's ability to pay its debts. If a company has low liquidity, it may struggle to pay its bills on time, which can result in
late fees and damaged relationships with suppliers.
Secondly, they are referenced in determining a company's creditworthiness. Lenders and creditors often use liquidity ratios to evaluate a company's ability to pay back loans or credit. A company with low
liquidity may not be able to secure credit or may have to pay higher interest rates.
Lastly, they can be compared to other financial ratios to provide a more comprehensive picture of a company's financial health. For example, a high liquidity ratio coupled with a low debt-to-equity ratio may indicate that a company has strong financial health.
What are Liquidity Ratios Used For?
Liquidity ratios are used for several purposes, including:
- •Determining A Company's Ability To Pay Its Debts - A company with low liquidity may struggle to pay its debts on time, which can lead to late fees and damaged relationships with suppliers.
- •Evaluating A Company's Ability To Manage Its Cash Flow - Effective management of cash flow may be more feasible for a company with high liquidity, whereas a company with low liquidity may encounter difficulties in meeting its financial obligations in a timely manner.
- •Assessing A Company's Operational Efficiency - Liquidity ratios can provide insight into how efficiently a company is managing its working capital. A company with high liquidity ratios may be able to manage its working capital more efficiently than a company with low liquidity ratios.
- •Helping Investors And Creditors Make Informed Decisions - Investors and creditors often use liquidity ratios to evaluate a company's financial health and creditworthiness. By comparing a company's liquidity ratios to industry benchmarks, they can make informed decisions about
whether to invest in or lend money to a company.
How to Assess a Company's Liquidity
To assess a company's liquidity, you need to calculate and understand its liquidity ratios. The three main liquidity ratios are the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio.
- •The current ratio is calculated by dividing a company's current assets by its current liabilities. If the ratio is 2:1 or higher, it's considered healthy, but if it's less than 1:1, it's risky.
- •By subtracting inventory from current assets and dividing the outcome by current liabilities, the quick ratio is obtained. If the quick ratio equals or exceeds 1:1, it is regarded as healthy. However, if the quick ratio is less than 1:1, it indicates that the company is at risk.
- •The cash ratio can be determined by dividing a company's cash and cash equivalents by its current liabilities. A healthy cash ratio is 0.5:1 or higher, while a cash ratio below 0.5:1 is
considered risky.
Comparing Liquidity Ratios to Industry Benchmarks
To fully assess a company's liquidity, it is essential to compare its liquidity ratios to industry benchmarks. Benchmarks can provide insight into whether a company's liquidity ratios are in line with other companies in its industry.
For example, the current ratio for a manufacturing company may be different from the current ratio for a software company. By comparing a company's liquidity ratios to industry benchmarks, investors and creditors can make more informed decisions about the company's financial health.
Liquidity ratios are important in assessing a company's financial health. They provide insight into a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations and manage its cash flow effectively. Current
liquidity ratios and acid-test or quick ratios are the most commonly used liquidity ratios. Liquidity in business is vital for a company's financial well-being, and liquidity ratios are the most commonly used tools to measure it.
These ratios can be used to determine a company's ability to pay its debts, evaluate its ability to manage its cash flow, and assess its operational efficiency. By comparing a company's liquidity ratios to industry benchmarks, investors and creditors can make more informed decisions about the company's financial health.