While many different operating systems support the use of RAID, most are limited in their compatibility.Apple's macOS and macOS Server only support RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 1+0.
A Look at RAID Parameters
RAID is a highly configurable and customizable platform. As such, it can be daunting for first-time users. In this case, it's best to stick with the default RAID parameters.
Mac RAID 0 parameters, for example, come with the default values of:
Advanced users are free to customize these settings to their likings. Particularly, the "Block size" parameter is often changed to a value of 16kb (32 sectors), 64kb (128 sectors), 128kb (256 sectors), or 256kb (512 sectors). While RAID 0 is the ideal choice for data striping, Mac users can also use RAID 1 for data mirroring.
RAID 0+1, sometimes called RAID 01, facilitates both data replication and data sharing between individual disks. A minimum of four disks are involved in a RAID 01 application – as opposed to the minimum of two seen in RAID 0 and RAID 1. RAID 0+1 is referred to as a nested RAID level or a hybrid RAID.
Data striping vs. Data mirroring
While RAID 0 focuses solely on data striping, RAID 1 involves data mirroring. It's important to understand the differences between these two processes in order to ensure you are making the most of your RAID setup.
Data striping: Data or disk striping involves the segmentation of sequential, disk-based data. This makes it possible to store consecutive sections of data across multiple physical disks. Although it doesn't offer any level of redundancy, it's a great strategy for improving system performance and data accessibility.
Data mirroring: The traditional form of backing up data via RAID, data mirroringuse multiple physical drives to store redundant copies of data. If an individual disk fails or experiences data corruption, an identical, up-to-date copy of that dataset can be called in from one of the backup disks. Instead of improving performance, data mirroring lets you achieve data redundancy and, ultimately, greater data security.
In the case of RAID 0+1, both data striping and data mirroring are used. In this scenario, half of the drives are used for striping while the others are used for mirroring. This application gives users the best of both worlds with greater data redundancy and improved system performance.
Now that you have a better idea of the common Mac RAID parameters and the compatible RAID configurations, as well as some further insight into the most common uses of RAID technology in the 21st century, it's time to put that knowledge to use and optimize your own RAID configurations as soon as possible.

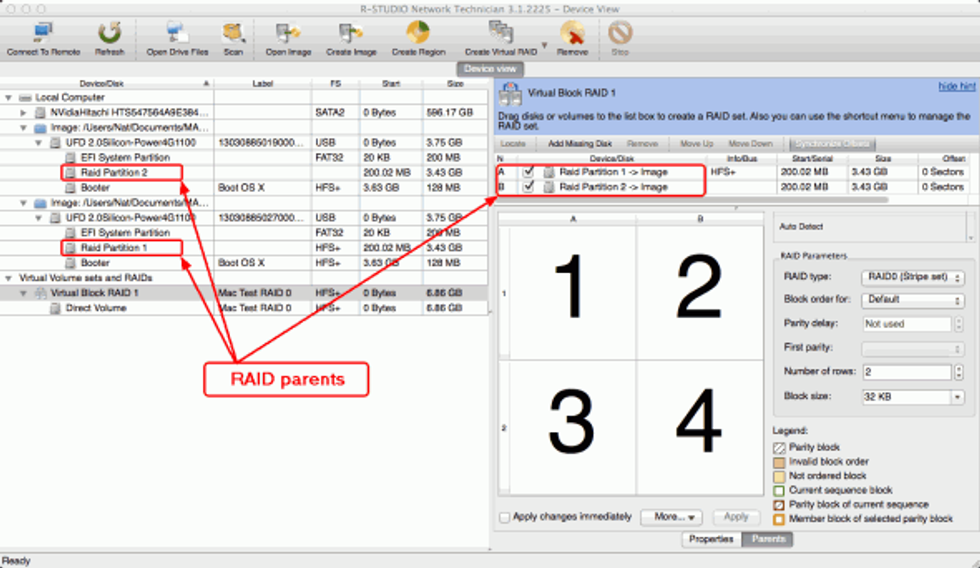




 Photo by
Photo by 









