Mars, Venus and Earth are all terrestrial planets, relatively small in size and closest to the sun. At one point in history, they were all suspected to be similar in atmospheric composition, making it possible for them to support life. Over time, two of the planets slowly changed as they adapted to atmospheric and geologic processes, as well as orbital and rotational motions. The temperatures and composition of atmosphere of each planet contributes to the Goldilocks problem. Venus is too hot, Mars is too cold and Earth is just right. There are many factors that influenced two planets to spiral to polar opposites of the spectrum and one to stay the same.
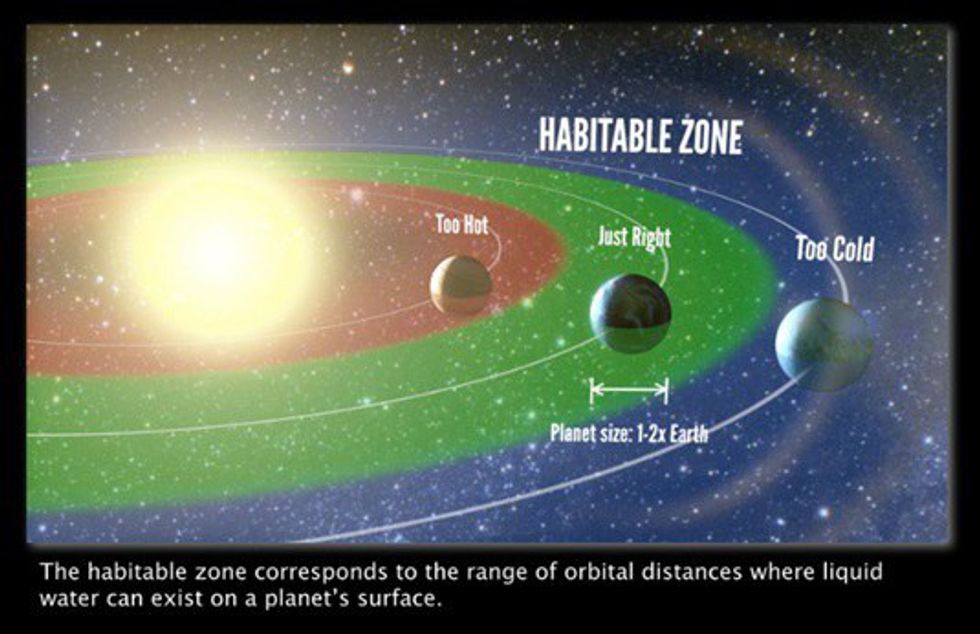
The “Goldilocks theory” is terminology used for describing the current state in which the terrestrial planets are. Venus, Earth, and Mars are approximately the same distance from the sun, which means they formed out of the same material and had around the same initial temperatures. Now Venus is too hot for life and Mars is too cold.
Recommended for you
Although currently Venus is similar to Earth in size and mass, there are many differences. The air pressure is 92 times the atmospheric pressure of Earth’s surface. This variation, among many others, weren’t present when the terrestrial planets first formed; Venus was much cooler with a greater abundance of water. However, due to Venus’s distance from the sun, the water never liquefied during the water table process and remained in the atmosphere as evaporate, which began greenhouse heating. This process is called runaway greenhouse (figure below). As the surface heated up, the carbon dioxide in the rocks was released, and as a result, the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enhanced the effect. This gradually turned into a positive loop, because as the atmosphere increased in carbon dioxide composition, it heated up the planet causing the rocks to bake and release more carbon dioxide.
There are many theories and high possibilities that Venus was once inhabited alongside Earth. They could have shared similar life forms, and it was more likely that Venus was able to support life than Mars.
Although Mars’ temperature is much colder than Earth’s, they have very similar compositions. They both have a dense, metallic core and an overlying mantle and crust composed of less dense materials. Mars and Earth both contain mountain ranges and sand dunes. After observing gullies and channels on Mars’ surface, scientists believe that liquid water used to flow through. Although there was evidence of water on the surface, Mars’ surface air pressure is much too low for pure liquid water to exist. However, the fact that it had sustained liquid water in the past, gives indication that the atmosphere was thicker and the surface was warmer from the greenhouse effect.
In 2013, NASA’s Curiosity rover provided data showing that the planet could have been habitable. The data was taken from drilling into a sample site nearby an ancient stream bed. The patch of bedrock contained fine-grained mudstone, and showed evidence of multiple periods of wet conditions.
While living on Mars may have been the case millions of years ago, the atmosphere changed over time as Venus did, and is now very cool and thin.
There are a few ways that Mars could have lost its atmosphere. One of them is that the low gravity of the planet let the atmosphere leak away into space. Another is that a lot of asteroid impacts could have blasted parts of the atmosphere away. Very large impacts could have occurred frequently in the solar system several billion years ago, and the energy could have been enough to push gas away from the planet.
The three terrestrial planets all began the same way, but do to their characteristics in composition and distance, they all ended up at either opposite ends of the spectrum or right in the middle. There are thoughts that Earth could end up like Venus because of the increased carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere. What happened to Mars and Venus wasn’t an anthropogenic contribution.
Eventually the Earth will take itself back, and return to the natural cycle. In millions of years it could follow in either path of the hot or cold planets-if something catastrophic were to occur.