With the craze of life, the world of politics is difficult to keep up with. The beginnings of President Trump's impeachment proceedings, however, have people attempting to stay updated more than usual. It is difficult to understand what's going on in today's news without a basic understanding of the impeachment process, but this process is more complicated than most people remember from their high school government classes. So, here is a brief description of how the impeachment process works.
First, a brief definition. Contrary to popular belief, impeachment itself does not end with removal from office. Impeachment, simply put, is a power of Congress to determine whether a civil officer's actions are reasonable to try him or her in court for removal from office. This power applies to any civil officer up to and including the president.
Step One: Investigation
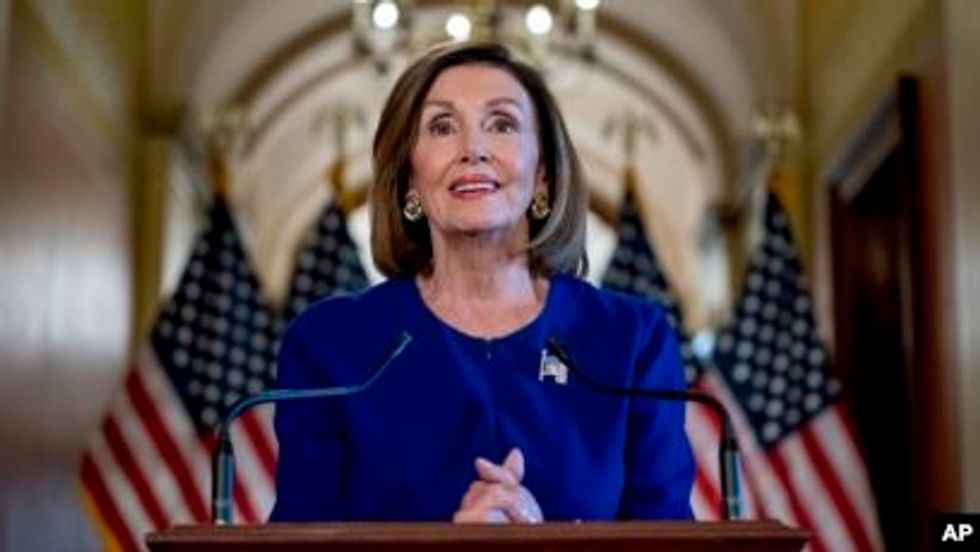

Speaker of the House, Nancy Pelosi, announces impeachment investigation into President Trump
The impeachment process begins with formal inquiry into the civil officer in question. This investigation can be conducted by a number of committees as seen fit by the Speaker of the House. These committees will thoroughly investigate the presidency and compile a collection of charges against the civil officer known collectively as The Articles of Impeachment. Finally, the Judiciary Committee must pass a vote on the articles in order to officially send them the the House for a vote.
Step Two: House Vote
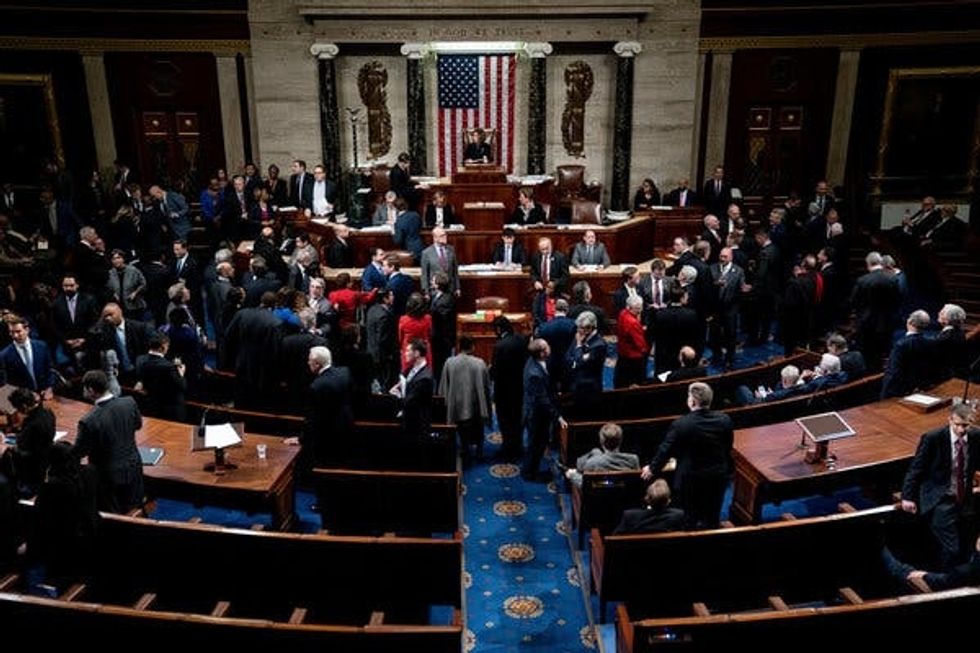

House of Representatives prepares to vote on Articles of Impeachment regarding President Trump
Once the Articles of Impeachment have been made official, they are sent to the House to be voted on. Members of the House of Representatives will vote on each charge to decide whether or not it should be tried in the senate. If none of the charges are passed in the House, the case is dropped and the investigation ends. If one or more of these articles is passed by a simple majority in the House, the civil officer in question is impeached.
Step Three: Senate Trial
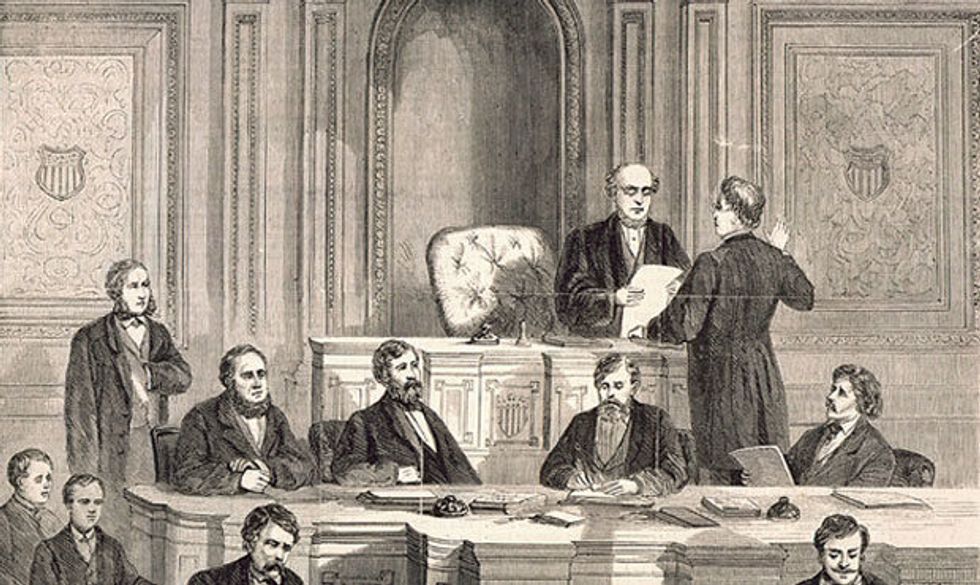

An illustration of the Senate impeachment trial of President Andrew Johnson
washington-impeachment-reaction-andrew-johnson
Impeachment means that the civil officer will now be put to trial by the Senate. The Senate trial will consist of a team of lawmakers appointed by the House of Representatives to play the role of the prosecutor, the White House defense lawyers, defending the civil officer in question, and the Senate, who will act as the jury. The Senate will vote on each charge separately. If one or more of the articles of impeachment is passed by a two-thirds majority, the civil officer in question is convicted and removed from office.
Step Four: Future Office
http://ourwhitehouse.org/the-presidential-oath-of-office/
The last power Congress is allowed by the constitution in the impeachment proceedings is the option to take a vote on the civil officer's ability to run for future office. After the Senate trial for removal from office has ended, the Senate may choose to vote on whether to disqualify the civil officer in question from future office. If the vote is held, it will require a simple majority to pass.
Only eight cases of impeachment have ended in conviction and removal from office. All eight cases were federal judges. While three U.S. Presidents have been impeached, none, so far, have been removed from office. Andrew Johnson and Bill Clinton were both impeached by the House but acquitted by the Senate. Congress began impeachment proceedings against Richard Nixon in the House. However, when his fate appeared sealed, Nixon stepped down from office before he could be formally impeached. Lastly, President Trump has been officially impeached by the House of Representatives. His trial in the Senate has not yet begun.
This is a very basic outline and history of formal impeachment proceedings. The US Constitution provides little more than a skeleton of how these procedures ought to be conducted, leaving most of the rules and regulations to be decided by the current Congress. In each case of impeachment, the House and Senate must vote on their rules of trial before investigations can begin.






















