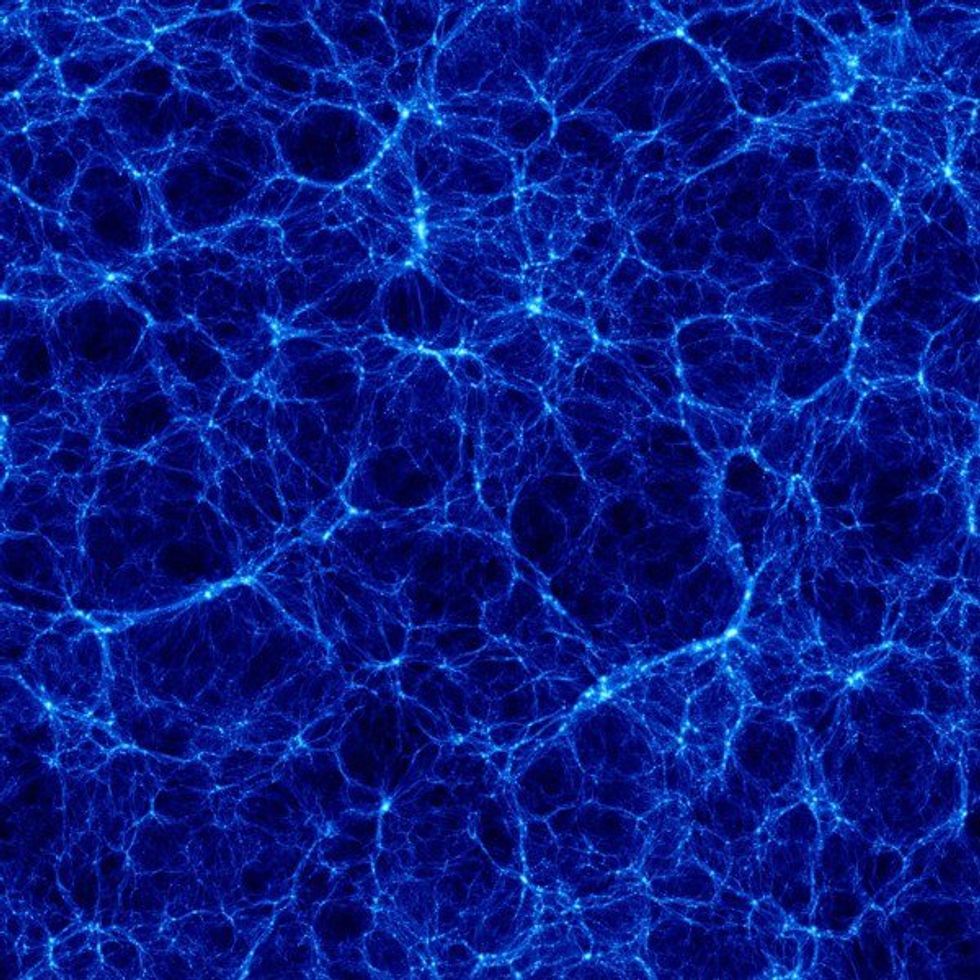
Dark Matter-
noun
1. a hypothetical form of matter invisible to electromagnetic radiation, postulated to account for gravitational forces observed in the universe.
Thanks Dictonary.com!
No one knows whether dark matter exists or not, and very few even know what it is. The name along with its natural connotation, however, only add to the mystery enshrouding dark matter.
Dark matter was discovered in 1933 by Fritz Zwicky, a Swiss scientist. It was originally called "Missing Mass." Theoretically, dark matter makes up about 27% of all mass in the universe.
Dark matter was named as such because no light can be seen from inside the mass, making it essentially...invisible. This is due to the fact that dark matter does not emit or absorb light or any other kind of electromagnetic energy. Because of this, we know far less than we would hope to know. Fortunately, with the aid of modern technology, we can see dark matter through x-rays.
We are always researching and learning more about the universe. And perhaps someday, we will find other life.
Sources:
How Dark Matter Works. (2007). HowStuffWorks. Retrieved 7 January 2017, from http://science.howstuffworks.com/dictionary/astronomy-terms/dark-matter.htm
dark matter | astronomy. (2016). Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 6 January 2017, from https://www.britannica.com/science/dark-matter