Even though we live in a country, in which the freedom to access and spread information is well-protected, we are still in danger of accepting narrow-minded opinions and convenient narratives. We will retreat to gated communities of like-minded people and reject all information that doesn’t affirm our viewpoint. The government isn’t manipulating us; the businesses aren’t manipulating us; the secret societies aren’t manipulating us. On the global forum created by the internet, we are deceived only by ourselves.
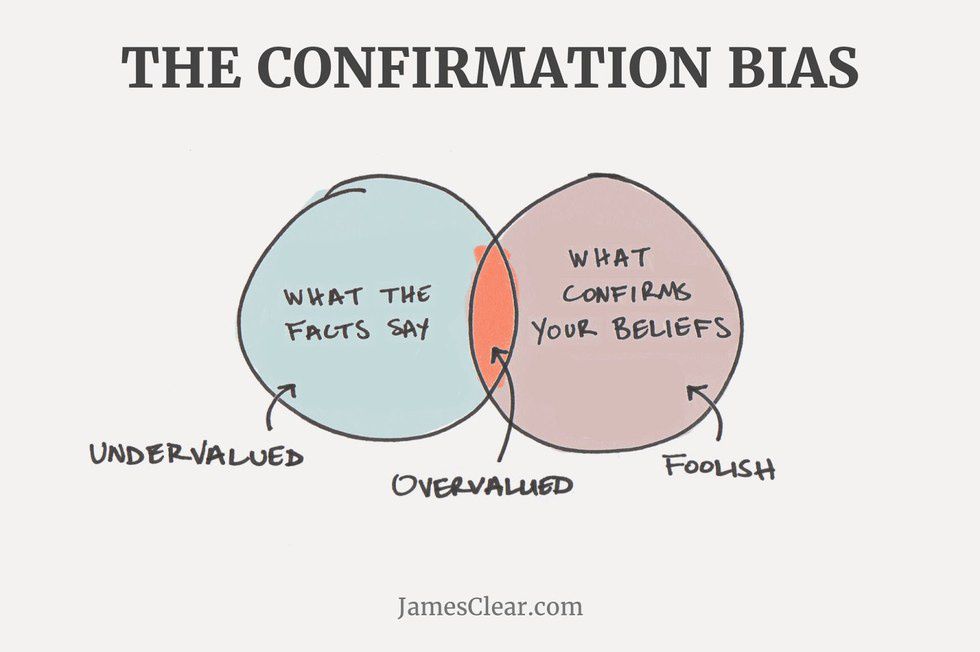
What I’m talking about is confirmation bias—“a type of selective thinking whereby one tends to notice and to look for what confirms one’s beliefs, and to ignore or undervalue the relevance of what contradicts one’s beliefs.” At its advent, the internet seemed like the perfect solution to confirmation bias. Since the web offered users the opportunity to disseminate and collect information on a global scale, it should have allowed the creation of a broader forum, in which diverse ideas and opinions could be exchanged. People should have become more open-minded through the internet.
Image Credit: http://bp.blogspot.com
But the resulting information overflow wound up depreciating the value of each piece of news or opinion. There was simply too much misinformation and junk data floating around for users to take at face value. All we want from this dizzying forum is truth in a convenient form of simplified reality—in a context that won’t upset us. The role of creating that context falls to social media, news aggregators and search engines.
These functions are programmed to give us the information we want to see to affirm our opinions. Using the subjects we search up on the internet, programmed algorithms expose us to related content that matches our interests. From news articles to social networking posts, all the content we see has already been selected for us. A narrative is created in our minds that may be built on prejudices or misinformation. The “truth” we find through the internet is more often than not an incomplete picture, and we’d never suspect that we can be wrong.
Image credit: younger-associates.com
The Millennials are especially vulnerable to this internet-enabled form of confirmation bias. As the first generation to truly grow up with the evolved form of the internet, we are highly influenced by and connected to social media. Much of our beliefs stem from long-time exposure to the content generated by those programmed algorithms. That’s partially why so many Millennials suspect Hillary Clinton is a corrupt crook and Donald Trump is an irrational fascist even without much tangible evidence to prove so. Social media and news aggregators simply propagate information that sells—even if they’re rumors, conspiracies, or dramatizations—according to our pre-existing notions.
But the consequences of confirmation bias extend past the creation of false narratives and a narrow-minded perception of information. Users will often congregate in homogeneous, polarized clusters known as “echo chambers”. These communities reinforce confirmation bias by compromising on the quality of information and proliferating “biased narratives fomented by unsubstantiated rumors, mistrust, and paranoia.”
In an extreme scenario, in which everyone has joined a gated community of like-minded people, the global forum no longer exists. Users only leave their echo chambers to diffuse information that supports their individual beliefs.
Everyone is proven right, but everyone is also wrong.
It’s a future that’s exactly contrary to what Millennials want from the web, yet we are the generation that has gotten closest to that scenario.
The internet still has the capability to become that global forum. There are many challenges, however, that complicate the exchange of information—data overflow, biased context creators, our own selective thinking. When we’re obsessed with causation and truth, we may ignore information that proves vital to seeing the whole picture.
Each and every one of us must decide whether to accept or to ignore the news presented to us. We have to question the narratives we follow and the beliefs we stand by. We have to accept that we can be wrong. The Millennials have been shaped by the internet, but they still have the freedom to create their own context.